Describe the Systemic and Pulmonary Blood Circulation Routes
In contrast the pulmonary circulation is composed of the vascular system that conducts blood from the right side of the heart through the lungs. 2 routes pulmonary systemic Closed.
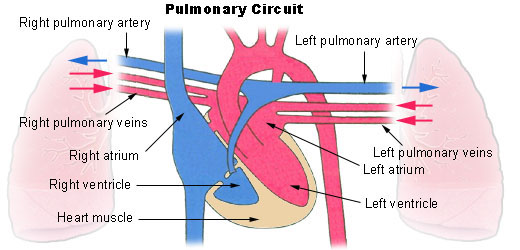
Seer Training Circulatory Pathways
In pulmonary circulation the arteries carry oxygen-poor blood and the veins bear oxygen-rich blood.

. Differentiate between the different portions of the cardiovascular system. In the lungs oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide eliminated and the oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins thus completing the circuit. It is responsible for carrying oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body and the deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body back to the heart.
The blood moves to the lungs exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen and returns to the left atrium. In the human heart two coronary arteries arise from the aorta just beyond the semilunar valves. In pulmonary circulation this deoxygenated blood is moved from the heart to the lungs where it.
The blood which is now low in oxygen is collected in veins and travels to the right atrium and into the right ventricle. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the rest of the body by the aorta. Deoxygenated blood travels from right ventricle to lungs via pulmonary arteries.
There is the pulmonary circulation which is in fact complimented by the systemic circulations. ROUTES OF CIRCULATION ANATOMY. As each atrium and ventricle contract blood is pumped into certain major blood vessels and from there continues through the circulatory system.
During diastole the increased aortic pressure above the valves forces blood into the coronary arteries and thence into the musculature of the heart. Systemic circulation starts in the left atrium when the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs arrives via the pulmonary veins. -systemic circulation- arteries and arterioles that carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to systemic capillaries and veins that return deoxygenated blood to the heart - pulmonary circulation- blood that is pumped out of the right ventricle through the pulmonary circulation.
The systemic circuit is the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body excluding the lungs. After moving through the pulmonary circuit oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle leaves the heart via the aorta. Pulmonary circulation path allows for blood circulation through the lungs for oxygenation of blood while systemic circulation path allows for blood circulation of the oxygenated blood through other.
The systemic circulation is composed of the vascular system supplied by the left ventricle that pumps blood into the aorta for distribution to the rest of the body. In the cardiovascular system the pulmonary circulation is a system of blood vessels that transport blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The blood passes to the left ventricle where it is pumped out through the aorta the major artery of the body taking oxygenated blood to the organs and muscles of the body.
This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. Pulmonary circulation systemic circulation and coronary circulation. There are two circulatory paths in the cardiovascular system namely pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation.
Pulmonary circulation is the system of transportation that shunts de-oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be re-saturated with oxygen before being dispersed into the systemic circulation. Lq Describe the 3 main routes of blood vessels. Pulmonary Circulation Route and Process.
The deoxygenated blood shoots down from the right atrium to the right ventricle. Deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body enters the heart from the inferior vena cava while deoxygenated blood from the upper body is delivered to the heart. The oxygenated blood shoots from the left atrium to the left ventricle below to begin.
WetcakeDigitalVision VectorsGetty Images. Arteries deliver deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange Path goes from right ventricle through pulmonary arteries lungs pulmonary veins to left atrium Hepatic portal circulation Unique blood route through the liver Vein hepatic portal vein exists between two capillary beds Assists with homeostasis of blood glucose levels. B Label the following in the diagram below.
Pulmonary Arteries Pulmonary Veins. The pulmonary arteries deliver oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs while the pulmonary veins deliver oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heartFor fetal circulation there is a special hole shunt called the ductus arteriosus that is between the pulmonary arteries and aorta to divert. Cardiac circulation pulmonary circulation systemic circulation arteries veins capillaries oxygenated blood deoxygenated blood.
Coronary circulation part of the systemic circulatory system that supplies blood to and provides drainage from the tissues of the heart. Pulmonary circulation consists of those blood vessels which are responsible for the transportation of blood through the lungs for the chance to be oxygenated and return the waste. The right ventricle pumps low-oxygen blood into the pulmonary artery which branches off into smaller and smaller arteries and capillaries.
Circulatory blood flow is segregated into two basic divisions. Left atrium of heart to left ventricle of heart to aorta to body organs to vena cava to right atrium of heart Pulmonary circulation. Pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
Humans and other mammals have two-circuit circulatory system s. In contrast in the systemic circulation which includes both the arteries and veins in the rest of the body blood is transported from a number of organs and tissues throughout your body to a common point in. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
This is where pulmonary circulation begins. One circuit is for pulmonary circulation and the other circuit is for systemic circulation the rest of the body. The heart then pumps it out of the right ventricle and into the pulmonary arteries to begin pulmonary circulation.
Start studying Circulatory Routes. Sections in this article. Systemic circulation is a part of the cardiovascular system in many complex organisms including humans.

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulations Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

What Is The Path Of Blood Through The Circulatory System

Bio121 Systemic And Pulmonary Circulations Flashcards Quizlet
Comments
Post a Comment